Family planning methods serve as a cornerstone of reproductive healthcare, offering individuals and couples the autonomy to make informed decisions about their reproductive journey. As key advocates for comprehensive and patient-centered care, nurses play a pivotal role in guiding individuals through the diverse landscape of family planning options.
This nursing notes aims to explore the different family planning methods available, their effectiveness, benefits, potential risks, and the critical role of nurses in fostering open dialogue, providing education, and supporting individuals in making choices that align with their unique reproductive goals and preferences.
Table of Contents
What are Contraceptive Methods?
Contraceptives, also known as birth control methods, are a class of medical interventions or devices used to prevent or decrease the likelihood of pregnancy. These methods work by interfering with the process of conception, either by preventing the release of an egg (ovulation), blocking the fertilization of an egg by sperm, or creating a hostile environment for the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus.
- A pregnancy test must be performed first to make sure that the woman seeking birth control is not presently pregnant.
- Assess for the OB history of the client, any past sexually transmitted diseases, the status of past pregnancies, and if they have used a family planning method that did not turn out effective.
- Assess subjectively the needs, preferences, desires, and feelings of the client regarding family planning.
- Assess the sexual practices of the client, the frequency, the number of their sexual partners, and if they have any allergies to latex.
Natural Family Planning
The natural family planning methods do not include any chemical or foreign body introduction into the human body. Most people who are very conscious of their religious beliefs are more inclined to use the natural way of birth control. Some want to use natural methods because it is more cost-effective.
Abstinence
- This natural method involves abstaining from sexual intercourse and is the most effective natural birth control method with an ideal 0% fail rate.
- It is also the most effective way to avoid STIs.
- However, most people find it difficult to comply with abstinence, so only a few of them use this method.
Calendar Method
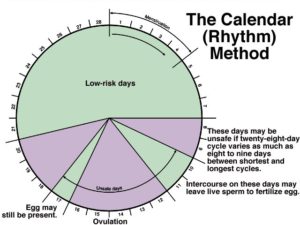
- Also called the rhythm method, this natural method of family planning involves refraining from coitus during the days that the woman is fertile.
- According to the menstrual cycle, 3 or 4 days before and 3 or 4 days after ovulation, the woman is likely to conceive.
- The process of calculating the woman’s safe days is achieved when the woman records her menstrual cycle for six months.
- She subtracts 18 from the shortest cycle and the difference is the first fertile day.
- She also subtracts 11 from the longest cycle, and this becomes the last fertile day.
- Starting from the first fertile day until the last day, the woman should avoid coitus to avoid conception.
- It has an ideal fail rate of 5%, but when used it has a typical fail rate of 25%.
Basal Body Temperature
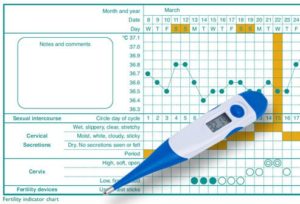
- The basal body temperature is the woman’s temperature at rest.
- BBT falls at 0.5⁰F before the day of ovulation and during ovulation, it rises to a full degree because of progesterone and maintains its level throughout the menstrual cycle, and this is the basis for the method.
- The woman must take her temperature early every morning before any activity, and if she notices that there is a slight decrease and then an increase in her temperature, this is a sign that she has ovulated.
- The woman must abstain from coitus for the next 3 days.
- The BBT method has an ideal fail rate of 9% and a typical use fail rate of 25%.
Cervical Mucus Method
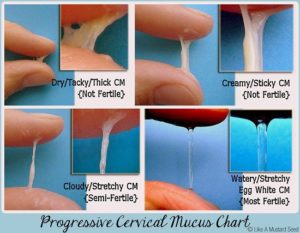
- The basis of this method is the changes in the cervical mucus during ovulation.
- To check if the woman is ovulating, the cervical mucus must be copious, thin, and watery.
- The cervical mucus must exhibit the property of spinnbarkeit, wherein it can be stretched up until at least 1 inch and feels slippery.
- The fertile days of a woman according to this method are as long as the cervical mucus is copious and watery and a day after it. Therefore, she must avoid coitus during these days.
- When used typically, it has a fail rate of 25%.
Symptothermal Method
- The symptothermal method is simply a combination of the BBT method and the cervical mucus method.
- The woman takes her temperature every morning before getting up and also takes note of any changes in her cervical mucus every day.
- She abstains from coitus 3 days after a rise in her temperature or on the fourth day after the peak of a mucus change.
- Symptothermal method has an ideal failure rate of 2%.
Ovulation Detection
- The ovulation detection method is an over-the-counter kit that can predict ovulation through the surge of luteinizing hormone that happens 12 to 24 hours before ovulation.
- The kit requires the urine specimen of the woman to detect the LH.
- The kit is 98% to 99% accurate and is fast becoming the method of choice by women.
Lactation Amenorrhea Method
- Through exclusive breastfeeding of the infant, the woman is able to suppress ovulation through the method of lactation amenorrhea method.
- However, if the infant is not exclusively breastfed, this method would not be an effective birth control method.
- It is also best to advise the woman that after 3 months of exclusive breastfeeding, she must make plans of choosing another method of contraception.
Coitus Interruptus
- This is one of the oldest methods of contraception.
- The couple still proceeds with the coitus, but the man withdraws the moment he ejaculates to emit the spermatozoa outside of the vagina.
- The disadvantage of this method is the pre-ejaculation fluid that contains a few spermatozoa that may cause fertilization.
- Coitus interruptus is only 75% effective because of this.
Hormonal Contraception
These hormonal contraceptives are effective through the manipulation of the hormones that directly affect the normal menstrual cycle so that ovulation would not occur.
Oral Contraceptives
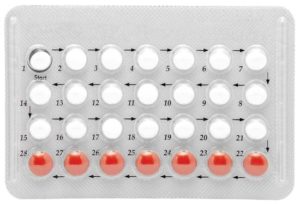
- Also known as the pill, oral contraceptives contain synthetic estrogen and progesterone.
- Estrogen suppresses the FSH and LH to suppress ovulation, while progesterone decreases the permeability of the cervical mucus to limit the sperm’s access to the ova.
- To use the pill, it is recommended that the woman takes the first pill on the first Sunday after the beginning of a menstrual flow, or the woman may choose to start the pill as soon as it is prescribed.
- Advise the woman that the first 7 days of taking the pill would still not have an effect, so the couple must use another contraceptive method on the initial 7 days.
- If the woman has skipped one day of taking the pill, she must take it the moment she remembers it, then still follow the regular use of the contraceptive.
- If the woman has missed taking the pill for more than one day, she and her partner must consider alternative contraception to avoid ovulation.
- Side effects of OCs are nausea, weight gain, headache, breast tenderness, breakthrough bleeding, vaginal infections, mild hypertension, and depression.
- Contraindications to OCs are breastfeeding, age of 35 years and above, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, smoking, diabetes, and cirrhosis.
Transdermal Patch
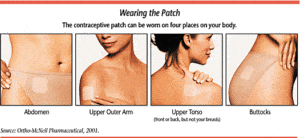
- The transdermal patch has a combination of both estrogen and progesterone in a form of a patch.
- For three weeks, the woman should apply one patch every week on the following areas: upper outer arm, upper torso, abdomen, or buttocks.
- In the fourth week, no patch is applied because the menstrual flow would then occur.
- The area where the patch is applied should be clean, dry, and free from any applications. And without any redness or irritation.
- Patches can be worn while bathing or swimming, but when the woman notices that the patch is loose, she should immediately replace the patch.
- If the patch has been loose for less than 24 hours, the woman need not use an alternative form of contraceptive, but if she is not sure of how long the patch has been loose, she should replace it and start with a new week cycle and also use an additional contraceptive method.
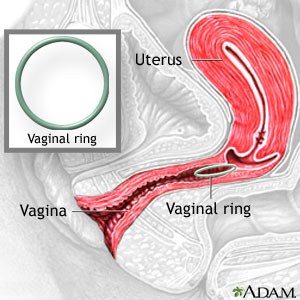
Vaginal Ring
- The vaginal ring releases a combination of estrogen and progesterone and surrounds the cervix.
- This silicon ring is inserted vaginally and remains there for 3 weeks, then removed on the fourth week as menstrual flow would occur.
- The woman becomes fertile as soon as the ring is removed.
- The vaginal ring has the same effectivity rate as oral contraceptives.
Subdermal Implants

- The subdermal implants are two rod-like implants embedded under the skin of the woman during her menses or on the 7th day of her menstruation to make sure that she is not pregnant.
- It contains etonogestrel, desogestrel, and progestin.
- It is effective for 3 to 5 years.
- Subdermal implants have a fail rate of 1%.
Hormonal Injections
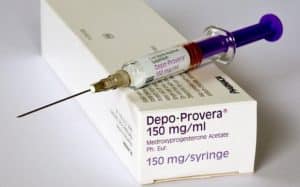
- A hormonal injection consists of medroxyprogesterone, and progesterone, and is given once every 12 weeks intramuscularly.
- The injection inhibits ovulation and causes changes in the endometrium and the cervical mucus.
- After administration, the site should not be massaged so it could absorb slowly.
- It has an effectiveness of almost 100%, making it one of the most popular choices for birth control.
- Advise the woman to ingest an adequate amount of calcium in her diet as there is a risk for decreased bone mineral density and to engage in weight-bearing exercises.
Intrauterine Device
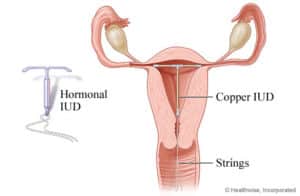
- An IUD is a small, T-shaped object that is inserted into the uterus via the vagina.
- It prevents fertilization by creating a local sterile inflammatory condition to prevent implantation.
- The IUD is fitted only by the physician and inserted after the woman’s menstrual flow to be sure that she is not pregnant.
- The device contains progesterone and is effective for 5 to 7 years.
- A woman with IUD is advised to check the flow of her menstruation every month and the IUD string, and also to have a pelvic examination yearly.
Chemical Barriers
- Chemical barriers such as spermicides, vaginal gels, creams, and glycerin films are also used to cause the death of sperms before they can enter the cervix and also lower the pH level of the vagina so it will not become conducive for the sperm.
- These chemical barriers cannot prevent sexually transmitted infections; however, they can be bought without any prescription.
- The ideal fail rate of chemical barriers is 80%.
Diaphragm
- A diaphragm works by inhibiting the entrance of the sperm into the vagina.
- It is a circular, rubber disk that fits the cervix and should be placed before coitus.
- If a spermicide is combined with the use of a diaphragm, there is a failure rate of 6% ideally and 16% typically.
- The diaphragm should be fitted only by the physician, and should remain in place for 6 hours after coitus.
- It can be left in place for not more than 24 hours to avoid inflammation or irritation.
Cervical Cap
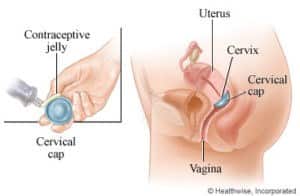
- The cervical cap is another barrier method that is made of soft rubber and fitted on the rim of the cervix.
- It is shaped like a thimble with a thin rim, and could stay in place for not more than 48 hours.
Male Condoms
- The male condom is a latex or synthetic rubber sheath that is placed on the erect penis before vaginal penetration to trap the sperm during ejaculation.
- It can prevent STIs and can be bought over the counter without any fitting needed.
- Male condoms have an ideal fail rate of 2% and a typical fail rate of 15% due to a break in the sheath’s integrity or spilling.
- After sexual intercourse, the condom is removed to be disposed.
Female Condoms
- These are also latex rubber sheaths that are specially designed for females and prelubricated with spermicide.
- It has an inner ring that covers the cervix and an outer, open ring that is placed against the vaginal opening.
- These are disposable and require no prescription.
- The fail rate of female condoms is 12% to 22%.
Surgical Methods
One of the most effective birth control methods is the surgical method. The two kinds of surgical methods are used by either the male or the female, and would ensure that conception is inhibited after the surgery for as long as the client lives.
Vasectomy
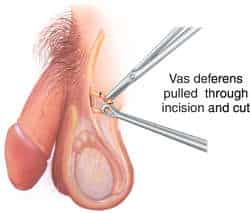
- Males undergo vasectomy, which is executed through a small incision made on each side of the scrotum.
- The vas deferens is then tied, cauterized, cut, or plugged to block the passage of the sperm.
- This procedure is done with local anesthesia, so advise the patient that mild local pain can be felt after the procedure.
- Advise the patient to use a back-up contraceptive method until two negative sperm count results are performed because the sperm could remain viable in the vas deferens for 6 months.
- There is a 99.5% accuracy rate for vasectomy and has a few complications.
Tubal Ligation
- In women, tubal ligation is performed by occluding the fallopian tubes through cutting, cauterizing, or blocking to inhibit the passage of the both the sperm and the ova.
- After menstruation and before ovulation, the procedure is done through a small incision under the woman’s umbilicus.
- A laparoscope is used to visualize the surgery, and the patient is under local anesthesia.
- The woman may return to her sexual activities after 2 to 3 days of the operation.
- Educate that menstrual cycle would still occur, and make sure that coitus before ligation is protected to avoid ectopic pregnancy.
- The effectiveness of this method is at 99.5%.
The reproductive system is our tool as humans to multiply or procreate. However, the earth would become unlivable if the growth of the population continues to boom. You have a choice among all these birth control methods, and these are only a call to be a responsible parent and citizen.

Thanks a lot Marianne
Life saver marianne
Term paper in public health… Check😅❤️
Thanks Marianne 💝
You are an Academic saver Mariane,
An inspiration for us in Health Courses.
Keep it up.
👏👏👏👏👏
Nice contents and explanation!!
Hi OtongJR,
Thanks so much! I’m glad you found the content and explanations on family planning helpful. By the way, are there any specific methods or aspects of family planning you’re interested in learning more about, or perhaps any challenges you think need more discussion?