Drug toxicity and overdoses are serious medical emergencies that demand immediate and effective treatment. Antidotes are specific substances used to neutralize the effects of poisons, including drugs. They help reverse toxic effects, prevent severe complications, and save lives.
The term antidote is a Greek word meaning “given against”. In nursing, especially for the NCLEX, understanding common drug antidotes and their mechanisms of action is important for providing competent and timely care.
What is an Antidote?
An antidote is a substance that can neutralize or counteract the harmful effects of a poison or toxin. It can work through various mechanisms, such as binding to the toxin, preventing its absorption, enhancing its elimination, or reversing its physiological effects. The appropriate use of antidotes is important in the management of poisoning cases and nurses must be well-versed in their indications, administration, and mechanisms of action.
How does an Antidote work?
Antidotes work through various mechanisms to counteract the effects of toxins or poisons in the body. Here’s a general overview of how antidotes work:
1. Neutralization.
Some antidotes directly neutralize the toxic substance by chemically reacting with it to form a less harmful or inert compound. For example, antacids like calcium carbonate can neutralize acidic substances.
2. Chelation.
Chelating agents bind to metal ions, such as heavy metals, in the body to form stable complexes that can be excreted in the urine. This helps remove toxic metals from the body. Examples include EDTA for lead poisoning and dimercaprol (BAL) for heavy metal poisoning.
3. Enhanced Elimination.
Certain antidotes enhance the elimination of toxins from the body by increasing their excretion through urine, bile, or other routes. For instance, activated charcoal adsorbs toxins in the gastrointestinal tract, preventing their absorption and facilitating their elimination via feces.
4. Receptor Blockade.
Some antidotes work by blocking the action of toxins at specific receptors in the body. For example, flumazenil blocks benzodiazepine receptors, reversing sedation and respiratory depression caused by benzodiazepine overdose.
5. Antagonism.
Antagonistic antidotes counteract the effects of toxins by opposing their actions directly. For example, vitamin K antagonizes the anticoagulant effects of warfarin by promoting the synthesis of clotting factors.
6. Metabolic Conversion.
Certain antidotes facilitate the metabolism of toxins into less toxic metabolites or promote the conversion of toxic substances into more easily eliminated forms. For example, acetylcysteine facilitates the metabolism of acetaminophen into non-toxic metabolites in cases of acetaminophen overdose.
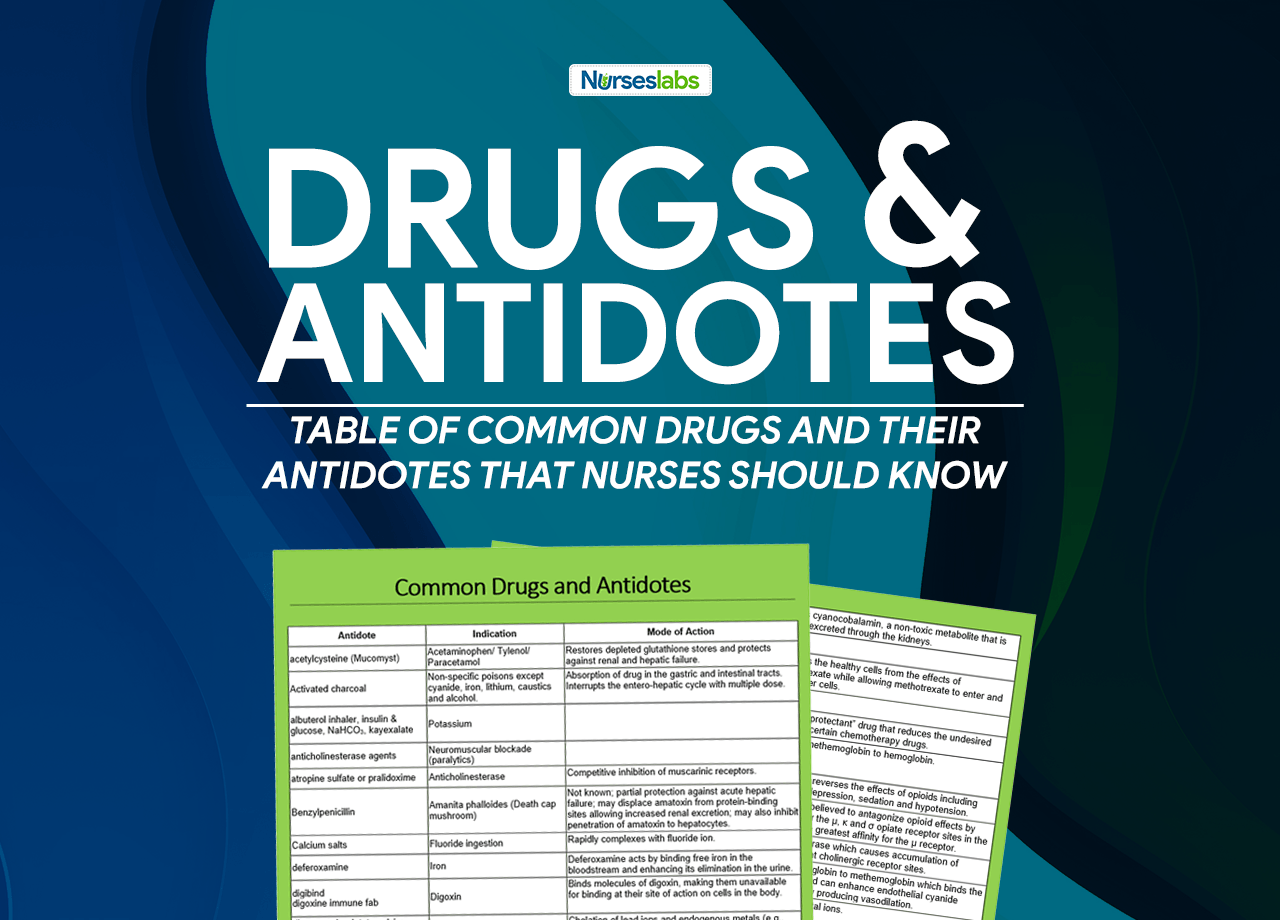
Common Drug Antidotes
Here is a list of common drug antidotes frequently encountered in clinical settings and relevant for the NCLEX exam, along with their mechanisms of action:
| Indication | Antidote | Mode of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen (Tylenol) toxicity | N-acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) | Acetylcysteine replenishes glutathione stores, enhancing the non-toxic metabolism of acetaminophen, thereby preventing liver damage. |
| Various oral poisonings and overdoses except for cyanide, iron, lithium, caustics, and alcohol. | Activated charcoal | Activated charcoal adsorbs toxins in the gastrointestinal tract, reducing their systemic absorption. |
| Cholinergic crisis, Organophosphate or carbamate insecticide poisoning, certain mushroom poisonings | Atropine (Atropen) | Atropine blocks acetylcholine receptors, reversing cholinergic effects like salivation, bronchial secretions, and bradycardia. |
| Magnesium Sulfate overdose, hyperkalemia, calcium channel blocker overdose | Calcium gluconate | Calcium gluconate stabilizes cardiac membranes and counteracts the effects of hyperkalemia and calcium channel blockers. |
| Fluoride ingestion | Calcium chloride or calcium gluconate | Calcium chloride binds to fluoride ions, forming insoluble calcium fluoride, reducing fluoride toxicity, especially on the cardiovascular and nervous systems. |
| Iron poisoning | Deferoxamine (Desferal) | Deferoxamine binds free iron in the bloodstream, forming a complex that can be excreted in the urine. |
| Digoxin toxicity | Digoxin immune fab (DigiFab/Digibind) | Digoxin immune fab binds to digoxin molecules, forming a complex that is then excreted by the kidneys, thereby neutralizing its effects. |
| Heavy metal poisoning, such as lead, arsenic, mercury, copper, and thallium. | Dimercaprol (BAL) | Dimercaprol chelates heavy metals, forming stable complexes that can be excreted in the urine, thereby reducing their toxicity. |
| Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) | Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) | Diphenhydramine blocks histamine (H1) and muscarinic (M1) receptors, which reduces the excessive cholinergic activity in the central nervous system that contributes to EPS. |
| Heavy metal poisoning, such as lead, copper, and mercury | D-penicillamine (Cuprimine) | D-penicillamine works by forming stable complexes with the metal ions, which are then excreted from the body. |
| Lead poisoning | Edetate calcium disodium (Calcium EDTA), dimercaprol (BAL), Succimer Dimercaptosuccinate (DMSA) | EDTA: Chelates lead by binding to it, forming a water-soluble complex that is excreted in the urine. |
| Benzodiazepine overdose | Flumazenil (Romazicon) | Flumazenil competitively inhibits benzodiazepine binding at the GABA receptor, reversing sedation and respiratory depression. |
| Ethylene glycol (antifreeze), Methanol poisoning | Fomepizole (Antizol) Ethanol, Hemodialysis | Fomepizole inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase, preventing the metabolism of toxic alcohols into their harmful metabolites. |
| Beta-blockers overdose, calcium channel blockers overdose, hypoglycemia | Glucagon | Glucagon increases cyclic AMP in cardiac cells, improving heart contractility and counteracting the effects of beta-blockers. |
| Insulin reaction | Glucose (Dextrose 50%) | Glucose rapidly raises blood sugar levels, providing immediate energy to counteract insulin-induced hypoglycemia and alleviate symptoms like dizziness and weakness. |
| Cyanide poisoning | Hydroxocobalamin (1st line) Nitrites and thiosulfate (2nd line) | Hydroxocobalamin binds to cyanide to form cyanocobalamin, a non-toxic compound that is excreted by the body. |
| Methotrexate toxicity | Leucovorin Calcium (folinic acid) | Leucovorin calcium acts as a folate precursor, counteracting methotrexate toxicity by restoring normal cell function, especially in rapidly dividing tissues like the bone marrow and GI tract. |
| Cyclophosphamide toxicity | Mesna | Mesna works by binding to acrolein, a toxic metabolite of Cyclophosphamide, preventing damage to the bladder and reducing the risk of hemorrhagic cystitis. |
| Chemical producing severe methemoglobinemia. Ifosamide-induced encephalopathy. | Methylene blue | Methylene blue works by reducing methemoglobin back to hemoglobin, restoring the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. |
| Opioids (Narcotic) overdose | Naloxone (Narcan) | Naloxone competitively binds to opioid receptors, reversing the effects of opioids like respiratory depression and sedation. |
| Anticholinergics | Neostigmine | Anticholinesterase which causes accumulation of acetylcholine at cholinergic receptor sites. |
| Carbon Monoxide poisoning | 100% Oxygen | Administering high-flow oxygen helps to rapidly displace carbon monoxide from hemoglobin, restoring oxygen delivery to tissues and reducing the risk of tissue hypoxia and organ damage. |
| Hypertensive crisis due to catecholamine excess (e.g., pheochromocytoma) | Phentolamine (Regitine) | Phentolamine blocks alpha-adrenergic receptors, causing vasodilation and reducing blood pressure. |
| Anticholinergic toxicity, Tricyclic antidepressants, anticholinergic, diphenhydramine dimehydrinate overdose | Physostigmine | A reversible anticholinesterase which effectively increases the concentration of acetylcholine at the sites of cholinergic transmission. |
| Warfarin (Coumadin) overdose | Phytomenadione (Vitamin K) | Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, reversing the anticoagulant effects of warfarin. |
| Organophosphate poisoning | Pralidoxime (2-PAM, Protopam) | Pralidoxime reactivates acetylcholinesterase that has been inactivated by organophosphates, restoring normal neuromuscular function. |
| Heparin overdose | Protamine sulfate | Protamine sulfate binds to heparin, forming a stable complex that neutralizes its anticoagulant effect. |
| Isoniazid overdose, monomethyl hydrazine poisoning. Adjunctive therapy in ethylene glycol poisoning. | Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) | Vitamin B6 serves as a cofactor for pyridoxal kinase, converting isoniazid (INH) into less toxic metabolites, thereby decreasing the risk of neurological side effects from INH overdose. |
| Cobra bite | Snake antivenom | Neutralizes venom by binding with circulating venom components and with locally deposited venom by accumulating at the bite site. |
| Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCA) overdose, salicylate poisoning, metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, chlorine gas inhalation | Sodium Bicarbonate | Sodium bicarbonate alkalinizes the blood and urine, enhancing the elimination of certain drugs and counteracting metabolic acidosis. |
| Alcohol-induced Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, acute thiamine deficiency | Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | Thiamine replenishes deficient levels, crucial for glucose metabolism, preventing and treating neurological damage in Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome and acute thiamine deficiency. |
Sources and References
- Chacko, B., & Peter, J. V. (2019). Antidotes in poisoning. Indian journal of critical care medicine: peer-reviewed, official publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine, 23(Suppl 4), S241.
- Buckley, N. A., Dawson, A. H., Juurlink, D. N., & Isbister, G. K. (2016). Who gets antidotes? choosing the chosen few. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 81(3), 402–407.
- Braitberg, G. (2019). Drugs and Antidotes in Acute Intoxication. Critical Care Nephrology, 574–588.e3.
Recommended Resources
Our recommended nursing pharmacology resources and books:
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase which will help support us. Thank you! For more information, check out our privacy policy.
Pharm Phlash! Pharmacology Flash Cards #1 BEST SELLER!
Test-yourself review cards put critical clinical information for nearly 400 of the top generic medications at your fingertips. And, you can count on them for accuracy, because each card is based on content from Davis’s Drug Guide for Nurses. Increase your test scores in pharmacology class.

Focus on Pharmacology (8th Edition)
Focus on Nursing Pharmacology makes challenging concepts more approachable. Engaging learning features cultivate your clinical application, critical thinking and patient education capabilities. This updated 8th edition builds on your knowledge of physiology, chemistry and nursing fundamentals to help you conceptualize need-to-know information about each group of drugs.

Pharmacology Made Incredibly Easy (Incredibly Easy! Series®)
Nursing pharmacology guide offers step-by-step guidance so you can grasp the fundamentals in enjoyable Incredibly Easy style. This is the perfect supplement to class materials, offering solid preparation for NCLEX® as well as a handy refresher for experienced nurses. Colorfully illustrated chapters offer clear, concise descriptions of crucial nursing pharmacology concepts and procedures.

Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care (11th Edition)
The Eleventh Edition of Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care provides a thorough understanding of key drugs and their implications for nursing care. This text, written by renowned nursing educators, helps you comprehend and apply pharmacology principles. A clear and engaging writing style simplifies complex concepts, making even the most challenging pharmacology content enjoyable. We recommend this book if you want a comprehensive nursing pharmacology guide.

Nursing Drug Handbook
Nursing2023 Drug Handbook delivers evidence-based, nursing-focused drug monographs for nearly 3700 generic, brand-name, and combination drugs. With a tabbed, alphabetical organization and a “New Drugs” section, NDH2023 makes it easy to check drug facts on the spot.

Pharmacology and the Nursing Process
The 10th edition of Pharmacology and the Nursing Process offers practical, user-friendly pharmacology information. The photo atlas contains over 100 unique illustrations and photographs depicting drug administration techniques. Updated drug content reflects the most recent FDA drug approvals, withdrawals, and therapeutic uses.

Mosby’s Pharmacology Memory NoteCards: Visual, Mnemonic, and Memory Aids for Nurses
The 6th edition of Mosby’s Pharmacology Memory NoteCards: Visual, Mnemonic, & Memory Aids for Nurses incorporates illustrations and humor to make studying easier and more enjoyable. This unique pharmacology review can be utilized as a spiral-bound notebook or as individual flashcards, making it ideal for mobile study.

See Also
Here are other nursing pharmacology study guides:
- Nursing Pharmacology – Study Guide for Nurses
Our collection of topics related to nursing pharmacology - Pharmacology Nursing Mnemonics & Tips
These nursing mnemonics aim to simplify the concepts of pharmacology through the use of a simple, concise guide. - Generic Drug Name Stems Cheat Sheet
Learn about these generic drug name stems to help you make sense of drugs easier! - Common Drugs and Their Antidotes
A guide to drug antidotes that nurses should be familiar about. - IV Fluids and Solutions Guide & Cheat Sheet
Get to know the different types of intravenous solutions or IV fluids in this guide and cheat sheet. - Drug Dosage Calculations NCLEX Practice Questions (100+ Items)
Care to take the challenge? This quiz aims to help students and registered nurses alike grasp and master the concepts of medication calculation.
We have a pill for that…
Drug Guides NEW!
Individual drug guides and nursing considerations for the most common medications used in nursing pharmacology:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Aspirin
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
- Furosemide (Lasix)
- Gabapentin
- Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
- Lisinopril
- Metoprolol
- Morphine
Gastrointestinal System Drugs
Respiratory System Drugs
- Antihistamines
- Bronchodilators and Antiasthmatics
- Decongestants
- Expectorants and Mucolytics
- Inhaled Steroids
- Lung Surfactants
Endocrine System Drugs
- Adrenocortical Agents
- Antidiabetic Agents
- Glucose-Elevating Agents
- Hypothalamic Agents
- Insulin
- Parathyroid Agents: Bisphosphonates, Calcitonins
- Pituitary Drugs
- Sulfonylureas
- Thyroid Agents
Autonomic Nervous System Drugs
- Adrenergic Agonists (Sympathomimetics)
- Adrenergic Antagonists (Sympatholytics)
- Anticholinergics (Parasympatholytics)
- Cholinergic Agonists (Parasympathomimetics)
Immune System Drugs
Chemotherapeutic Agents
- Anthelmintics
- Anti-Infective Drugs
- Antibiotics
- Antifungals
- Antineoplastic Agents
- Antiprotozoal Drugs
- Antiviral Drugs
Reproductive System Drugs
Nervous System Drugs
- Antidepressants
- Antiparkinsonism Drugs
- Antiseizure Drugs
- Anxiolytics and Hypnotic Drugs
- General and Local Anesthetics
- Muscle Relaxants
- Narcotics, Narcotic Agonists, and Antimigraine Agents
- Neuromuscular Junction Blocking Agents
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs
Cardiovascular System Drugs



































11 responses to “Common Drugs and Their Antidotes Cheat Sheet”
a.a.can u please send me some guidelines for the establishment of poison contrl center in a hospital?
thanks
can u please send me all natidote for all drugs thanks
Magnesium sulfate – calcium gluconate… to add in the list :)
Would anyone post Drug of choice for specific disease or condition here. thanks :)
Exellent job, thanks
Antidote for Heparin is Protamine SO4 right?
Hey Matt!
I was wondering if the printable cheat sheet for this is still available.
How can I download this as a pdf or some easily printable format?
I’m wondering too!
Matt, you cannot imagine how helpful your work is for all us student nurses. Thanks a ton, I wish you all the best in life.
so helpful, thank you
I am interested in developing generic form of Antidotes to avoid the fatal effects of drug abuse. It will be nice if the names of a few of such antidotes drug substances can be shared.
Will also look at the possibilities of development of the drug substances reported in this list at low cost.