Computed tomography (CT) scan, also known as computerized axial tomography (CAT), or CT scanning computerized tomography is a painless, non-invasive diagnostic imaging procedure that produces cross-sectional images of several types of tissue not clearly seen on a traditional X-ray.
CT scans may be performed with or without contrast medium. A contrast may either be an iodine-based or barium-sulfate compound that is taken orally, rectally, or intravenously which can enhance the visibility of specific tissues, organs, or blood vessels. The duration of the procedure will depend on the area being scanned.
The roles and responsibilities of a nurse extend throughout the whole duration of the CT scan procedure — from taking patient’s history, obtaining informed consent, preparing the patient, and providing education. To ensure the safety and accuracy of the procedure, learn about the nursing interventions and concepts behind computed tomography (CT) scan.
Procedure
The protocol and procedures for computed tomography (CT) scan varies per area but generally, the following steps are followed:
- The patient is positioned on an adjustable table inside an encircling body scanner (gantry); straps and pillows may be used to help in maintaining the correct position.
- The patient may be instructed to hold his breath during the scanning.
- A series of transverse radiographs are taken and recorded
- The information is reconstructed by a computer and selected images are photographed.
- Once the images are reviewed, an I.V. contrast enhancement may be ordered and additional images are obtained.
- The patient is assessed carefully for adverse effects to the contrast medium.
Types
The following are the different types of computed tomography (CT) scans:
Abdominal and pelvic
CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis combines radiologic and computer technology to determine the cause of unexplainable abdominal or pelvic pain and diseases of the bladder, uterus, liver, colon, small bowel, and other internal organs.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Bone and skeletal
Computed tomography (CT) scan of the bone is indicated to provide information and assess the severity of different bone diseases and conditions such as fractures, cancer, and infection.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
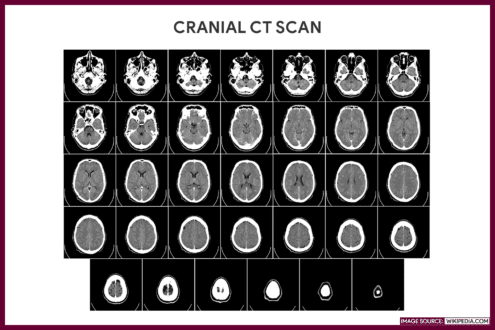
Brain
Also known as “cranial CT scan” or “Head CT”. It is indicated to provide detailed information on head injuries, stroke, brain tumors and other diseases affecting the brain.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Cardiac calcium scoring
The goal of a cardiac CT for calcium scoring is to detect coronary artery disease (CAD) at an early stage in individuals who do not yet have any symptoms but are at risk for the disease. Calcium Scoring is most often suggested for males aged 45 years or older, and for females aged 55 and over.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Ear
In CT scan of the ear, the radiologist is able to diagnose conditions such as chronic otitis media, ear infections, cholesteatoma, conductive hearing loss, mastoiditis, and cochlear implants.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
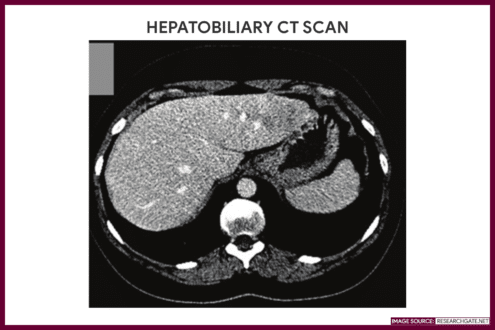
Liver and Biliary Tract
CT scan of the liver and biliary tract provides an in-depth information about the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and other related structures.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Orbital
An orbital CT scan provides detailed information about the eye sockets, eyes, and adjacent bone structures.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Pancreas
CT scan of the pancreas may be useful to diagnose cancer of the pancreas, and pancreatitis, and to differentiate pancreatic problems and disorders of the retroperitoneum.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Renal
A renal scan examines the structural and functional abnormalities of the kidney. It is indicated to detect tumors, obstructions, and lesions.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
Spinal
CT scan of the spine is performed to gain insight regarding the vertebrae and other spinal structures and tissues. It is indicated to detect spinal related injuries and diseases of the spine.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
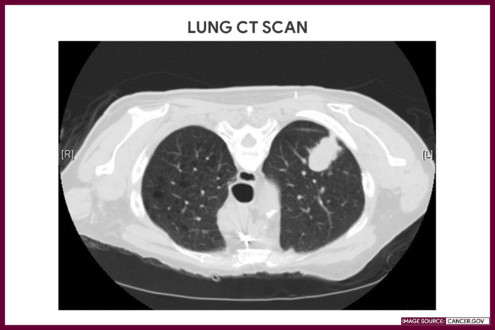
Thoracic
CT scan of the chest aids in determining the cause of an unexplained cough, fever, difficulty of breath, chest pain, and other respiratory symptoms. It is recommended for screening of possible lung cancer in its early, curable stage.
| Indication | Abnormal Results |
|
|
Contraindication
Computed tomography (CT) is contraindicated in:
- Pregnant patient (absolute contraindication)
- Patients with a known allergy to iodine
- Patients with claustrophobia
- Patients with renal impairment unless the benefits outweigh the risks
- Patients with hyperthyroidism or toxic goiter (induce thyrotoxic crisis)
- Patients with complications after a previous administration of a contrast
- Patients with severe obesity (usually more than 300 pounds)
Interfering Factors
- Retained oral or I.V. contrast material from previous diagnostic studies may affect the visibility of the images.
- Metal objects including eyeglasses, dentures, jewelry, and hairpins
Nursing Responsibilities for CT Scan
The following are the nursing interventions and nursing care considerations for a patient undergoing computed tomography:
Before the procedure
The following are the nursing interventions before computed tomography:
- Informed Consent. Obtain an informed consent properly signed.
- Look for allergies. Assess for any history of allergies to iodinated dye or shellfish if contrast media is to be used.
- Get health history. Ask the patient about any recent illnesses or other medical conditions and current medications being taken. The specific type of CT scan determines the need for an oral or I.V. contrast medium
- Check for NPO status. Instruct the patient to not to eat or drink for a period amount of time especially if a contrast material will be used.
- Get dressed up. Instruct the patient to wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing during the exam.
- Provide information about the contrast medium. Tell the patient that a mild transient pain from the needle puncture and a flushed sensation from an I.V. contrast medium will be experienced.
- Instruct the patient to remain still. During the examination, tell the patient to remain still and to immediately report symptoms of itching, difficulty breathing or swallowing, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and headache.
- Inform about the duration of the procedure. Inform the patient that the procedure takes from five (5) minutes to one (1) hour depending on the type of CT scan and his ability to relax and remain still.
After the procedure
The nurse should be aware of these post-procedure nursing interventions after computed tomography (CT) scan:
- Diet as usual. Instruct the patient to resume the usual diet and activities unless otherwise ordered.
- Encourage the patient to increase fluid intake (if a contrast is given). This is so to promote excretion of the dye.
Normal Results
The following are the expected normal results of computed tomography (CT) scan
- Specific type of CT scan reveals normal findings
- Normal findings on a CT scan shows bone (which has the densest tissue) appears as white areas. Tissues densities will show as shades of gray, and fat tissue appear as black or dark gray. Cerebrospinal fluid (has no tissue) will appear as black. Air will also look black and darker than fat.
Abnormal Results
The abnormal results of a computed tomography (CT) scan varies per area.
- The specific type of CT dependent on the area of study (see abnormal results above).
Gallery
Images related to computed tomography (CT) scan.


References
Additional resources and references for this guide:
- Calcium Scoring. (2018). Stmaryhealthcare.org. Retrieved 01 October 2018, from https://www.stmaryhealthcare.org/calciumscoring
- CT scan – Mayo Clinic. (2018). Mayoclinic.org. Retrieved 01 October 2018, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
- What are the Radiation Risks from CT?. (2018). Fda.gov. Retrieved 01 October 2018, from https://www.fda.gov/
- CT Scan Overview — Health Center, University of Connecticut. (2018). Fitsweb.uchc.edu. Retrieved 12 October 2018, from https://fitsweb.uchc.edu/ctanatomy/extrem/index.html
- Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2009). Critical care nursing in a flash. Philadelphia.




































Leave a Comment